

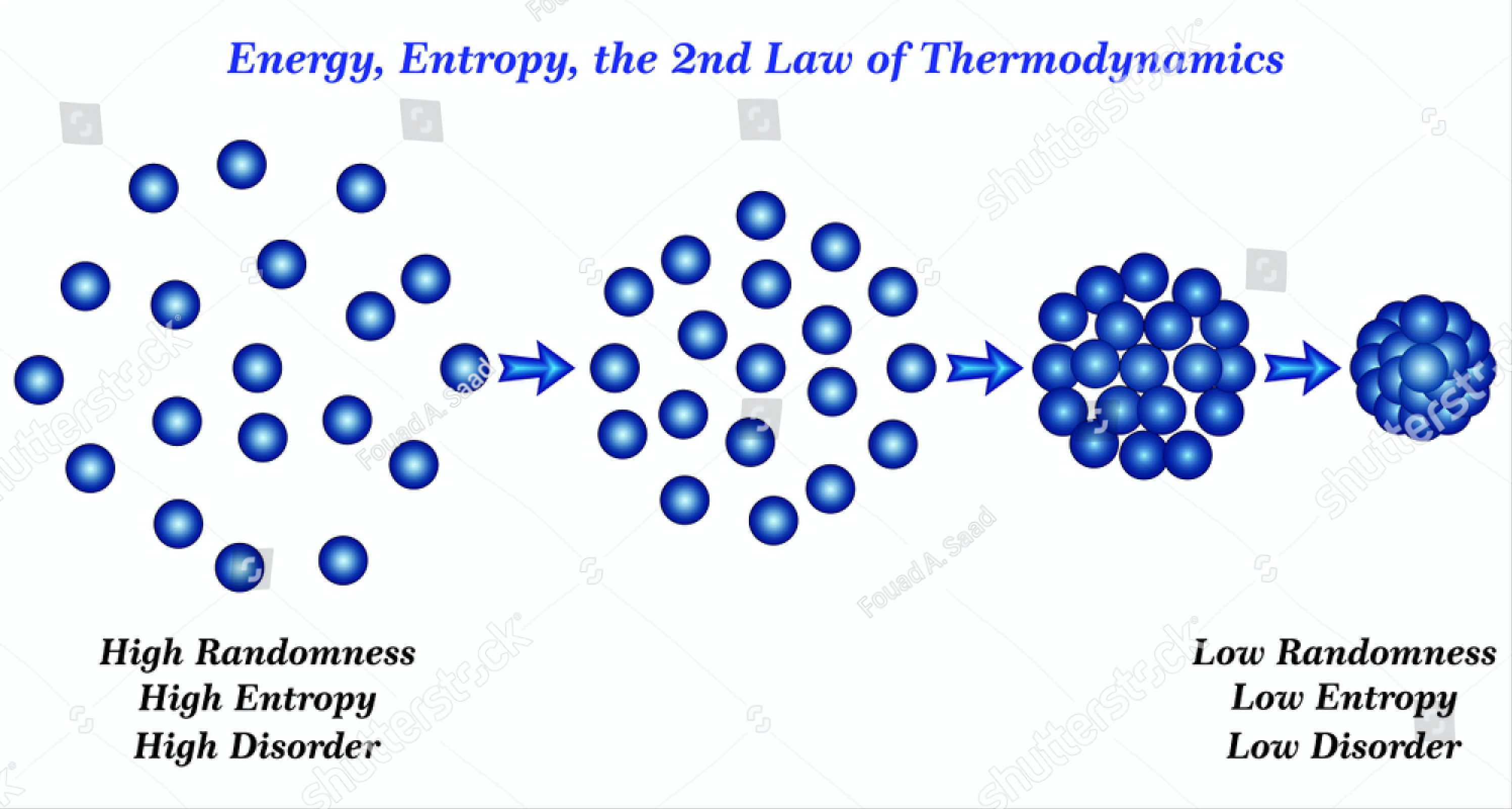
Shows that different types of energy are not equivalent in terms of theĪbility to transform into other forms of energy. Milk will never flow back into the glass.ĭeck of cards can never be shuffled back in the original order. Second law of thermodynamics: entropy increase.īroken window will never spontaneously recover. (W) Ask the class: Analyze and explain everyday examples illustrating the Second law is sometimes called the "arrow of time." Second law of thermodynamics fixes the direction of time only forward, in the Second law of thermodynamics says that the total entropy of a closed systemĬan only increase or remain unchanged (Boltzmann Equation). Seeming simplicity, is one of the most difficult and often misunderstood laws The Universe lies in the second law of thermodynamics, which, for all its The reason for such irreversibility of the processes occurring in Perfume fills the room - but you cannot collect it back into the bottle. Not difficult to break eggs and make scrambled eggs, but it is impossible to With a lower temperature, but never vice versa. Is transferred spontaneously from bodies with a higher temperature to bodies Processes associated with the flow of heat are irreversible. The cooling were reversible, cold coffee could spontaneously heat up, This means that events like breaking eggs are irreversible.Įgg cannot spontaneously return to a more ordered state.īut a cold cup of coffee will never warm up spontaneously. īring students to the independent formulation of a conclusion.Ī conclusion: The total entropy of the system must always В ) Determine the entropy change ΔS air in the room. А ) Determine the entropy change ΔS cup of coffee. Suppose a cup of coffee with a temperature 80 0С cooling in a room with a temperature 20 0С, loses Q =1000 J heat.

When deciding students D iscuss the solution in pairs, then hold a general discussion with the teacher. Transferred in the process to the temperature at which this process took Those the entropy change is equal to the amount of heat Thermodynamics, entropy is a quantity determined by the ratio: Increases with temperature as well as with volume. Higher entropy than solids, and gases have the highest entropy. A broken egg has more entropy than a whole egg. Įntropy determines system disorder - the number ofĭifferent ways particles can be located in a system. Not? Why are some phenomena possible and others not? ( Т ) The answer is entropy. Have you ever seen how a broken egg or a broken plate becomes whole again? It happen to you that you broke an egg or accidentally broke a cup or plate? Is a process that allows the system to return to its original state without This were possible, the process would be reversible. Thus, the equilibrium reversible processes are an abstraction due to existing The absence of friction, all mechanical processes would proceed reversibly. The beginning of the lesson, return to the concept of reversible andĬycles do we most often encounter in real life? What cycles do heat engines The second law of thermodynamics in the analysis of thermodynamic processes. The meaning of the second law of thermodynamics The wording of the second law of thermodynamics Of the lesson topic: Reversible and irreversible processes. Very important to speak through each stage of work on a structural task !!!!
J? (no, since in the area 3-1 external forces performed work on the gas, andĭuring the isochoric cooling it gave off heat).

Has the internal energy of a gas changed for a cycle? Can we say that then,ĭuring the cycle, the gas received an amount of heat equal to 4 * 10 5 Work did the gas do during the isobaric expansion? (4∙10 5 J ) The gas temperature and volume in the second state. The amount of substance of the gas (60,2 mol) In state 3, it occupies a volume two times larger than in the first one and In the first state, the gas is under pressure ofĠ.8 ∙ 10 5 Pa, occupying a volume of 5 m 3. The graph shows the process of transition of an ideal gas of constant massįrom the state of 1-2-3-1. Ways of changing internal energy, The first law of thermodynamics. Thinking through the creation of a problem situation Physical quantities and their units of measurement. With mathematics: working with formulas, the standard form of numbers, Knows the wording of the second law of thermodynamics Ĭan explain the meaning of the second law of thermodynamics Īpplies the second law of thermodynamics in the analysis of thermodynamicĬooperation, respect, tolerance in relationships with classmatesĬarried out through / through a discussion of the key points of the topic in The formula for the efficiency of a heat engine for solving problems. To describe the Carnot cycle for an ideal heat engine Objectives that are achieved in this lesson (link to the curriculum)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
